We’ve all heard how too much salt impacts your health. We know we should watch what we eat and be careful about reading labels when it comes to the amount of sodium we take in.
However, 9 out of 10 Americans still eat too much sodium daily.
The recommended daily intake of sodium is 1,500 mg or less and 90% of Americans are eating roughly 3,400 mg. That’s more than double what we should be getting.
And that’s scary for our health.
How Too Much Salt Impacts Your Health
Approximately 65% of our salt intake comes from store bought foods like pre-made meals, soups, etc. According to recent research, more than half of all calories consumed in the United States comes from “ultra-processed” foods. Processed foods add artifical flavors and colors, sweeteners, preservatives and additives while increasing the amount of sodium in the diet.
Being unaware and not reading nutrition labels can hurt us more than they help us with convenience.
Overabundance of salt in your diet can result in various health problems. Unfortunately unlike other substances like certain vitamins, the body can’t just flush out the excess when it comes to sodium.
High Blood Pressure and Heart Disease
Studies have shown there are strong correlations between high sodium intake and high blood pressure and heart disease.
As you eat more sodium, the sodium content in your bloodstream rises and makes it more difficult for your kidneys to remove the excess water and sodium from body which can lead to serious health complications.
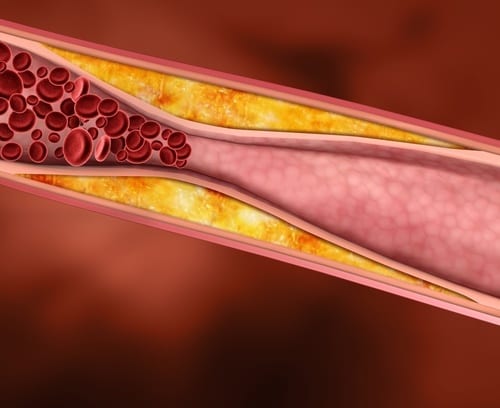
Excess sodium gets stored in the blood. The sodium causes strain on the blood vessels by creating thicker blood and even building up on arterial walls.
As a result, the arteries can begin to thicken and lose flexibility, adding more strain on the blood vessels and increasing blood pressure. This can put added stress on the heart and reduces oxygen deliverability throughout the body.
Decreased oxygen and blood to the heart can result in high blood pressure, heart disease, or heart attack.
Accelerated Dehydration
Excess sodium dehydrates your body faster than with normal amounts of sodium. When there is too much sodium in the bloodstream, the blood thickens and dilutes the amount of water available.
Less water in the body will weaken muscles and cause fatigue for the body. It can also speed up your heart rate, causing thickened blood to try to flow faster and puts stress on the heart and blood vessels.
However, the severity of dehydration also depends on how much water you’re drinking and how much you’re sweating.
Staying hydrated is extremely important to keep your blood balanced and keep sodium from building up in your blood vessels.
Kidney Damage and Disease
The kidneys function is to create and stabilize a balance of water, sodium, and potassium in the blood by excreting any excess.
Too much salt impacts your health and your kidneys by throwing off this delicate balance and not being able to filter enough salt. The excess sodium puts a heavy strain on the kidneys and can result in kidney damage or kidney disease.
In addition to kidney damage, build up of salt in the kidneys can create renal stones (kidney stones made of sodium). Calcium stones are more common, but too much salt can solidify in the kidneys as renal stones, which are equally as painful.
How to Eat Less Sodium
If you tend to go for salty foods or buy store bought pre-prepared meals, take notice of where you can change these habits.
Lowering your sodium is possible and food tastes just as good without it. You’ll notice how too much salt impacts your health and how eating less will help it!
To learn more, read one of our other posts on how to eat less sodium.
Resources:
http://www.livestrong.com/article/360301-dehydration-and-sodium-levels/
http://www.worldactiononsalt.com/salthealth/factsheets/kidney/

